Mineral insulated ACSR Cable, the full English name is mineral insulated cable, and the abbreviation is (MI) cable.
Due to its complex process, high production cost and much higher market price than conventional YJV and yjy cables, it was rarely used in China at the initial stage and was only used in important places with high requirements for safety conditions. Later, it was clearly required to be used under certain conditions due to the implementation of code for fire protection design of buildings gb50016-2014, which was widely popularized.
But for most engineers who do design, they often know to use it, but their understanding of it is not as good as YJV cable.
(1) Structural form
It is a kind of cable that uses copper sheath to wrap copper conductor core wire, and uses magnesium oxide powder as inorganic insulating material to isolate conductor and sheath (that is, magnesium oxide insulating layer is between core conductor and copper sheath). The outermost layer can select appropriate outer sheath as required.
See the following figure:
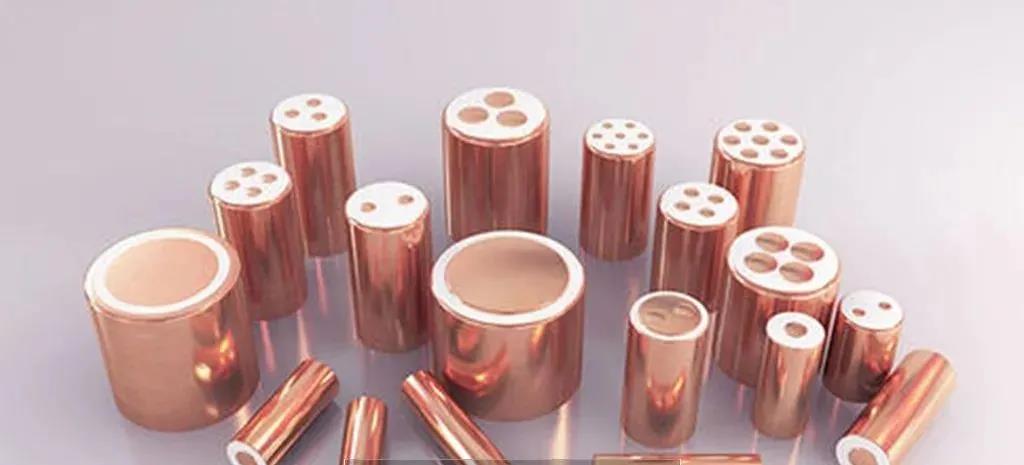

Mineral insulated (MI) cable
There is also a similar cable, which uses metal sheath instead of copper sheath to wrap conductor core wire and magnesium oxide insulation layer, which is called [mineral insulated metal sheathed cable].
(2) Performance and characteristics
1. Fire resistance
From the above structural form, mineral insulated cable does not contain organic materials, so it has the characteristics of non combustion, smokeless, non-toxic and fire resistance.
The melting point of copper is 1083 ℃, and the melting point of mineral insulating layer is above 1000 ℃, while the maximum temperature at the fire site of general civil buildings is below 1000 ℃. In this way, the copper sheath of the secondary layer can withstand the high temperature at the fire site.
The common fire-resistant cable, also known as organic insulated fire-resistant ACAR Cable, generally has a fire-resistant temperature of 750 ~ 800 ℃ for 90min. Therefore, the fire resistance of mineral insulated cable is quite excellent, and it is safe to use it in the fire area below the melting point of copper.
2. High temperature resistant operation
We know that the current carrying capacity and working temperature of the core are actually taken from the withstand temperature of the cable insulation layer. The higher the withstand temperature of the insulation layer, the greater the current carrying capacity.
Mineral insulated cable can withstand continuous working temperature up to 250 ℃ according to different application places. Under special circumstances, the AAAC Cable can maintain operation for a short time at a temperature close to the melting point of the copper sheath. It is very suitable for laying in high temperature places, such as metallurgy, boiler, glass furnace, blast furnace and so on.

3. Long life
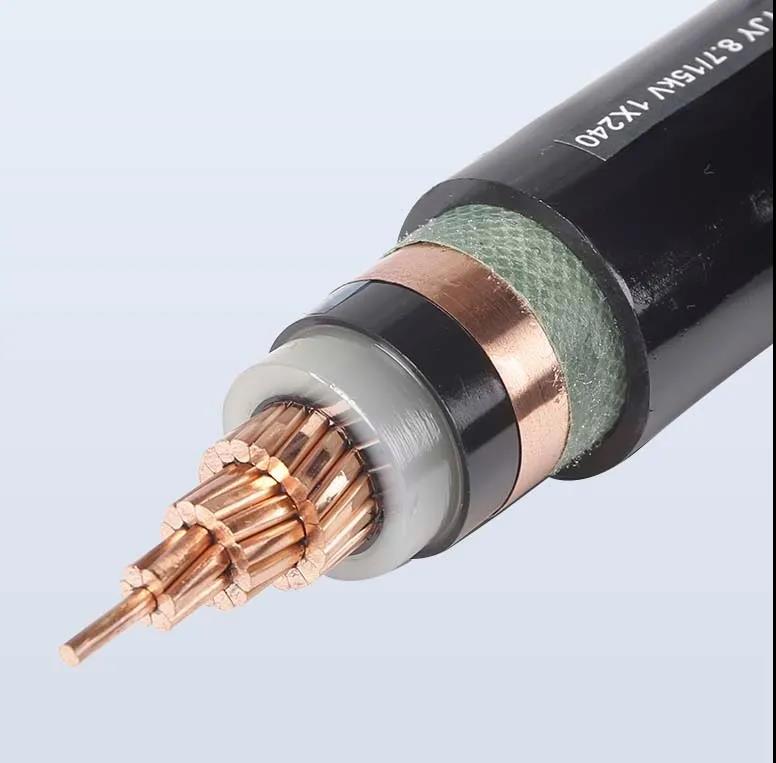
The inorganic materials used in the insulating layer and sheath layer of mineral insulated cable can make it more stable and longer service life.
4. Waterproof, explosion-proof and high mechanical strength
The insulating layer of mineral insulated cable is processed by high-density compaction process, and then protected by seamless copper sheath. In the product standard, it must meet the three requirements of fire resistance, spray resistance and mechanical impact, and can withstand severe impact and mechanical damage.
(3) Classification and model
According to the cable structure, it can be divided into [rigid] and [flexible]. As the name suggests, rigid mineral insulated cables are very difficult to bend during construction and installation, while flexible cables are relatively easy to lay, and their structural profile
Rigid mineral insulated cable is marked as [BTT] type, and flexible mineral insulated cable is marked as [RTT] type.
National standard GB / T 13033-2007 rigid cable models: light load 500V bttq, bttvq, bttyq, heavy load 750V bttz, bttvz, bttyz. 500V and 750V here refer to the voltage between the core conductor and the sheath and between each conductor does not exceed 500V and 750V.
The models of flexible cables in the national standard GB / T 34926-2017 are rttz, rttyz and rttvz, and the voltage levels are 0.6/1kv or 450 / 750V.
The models of other flexible cables are named by each manufacturer. There are more than ten common types, such as bttrz, bbtrz, yttw, ng-a (btly), etc.
From the above, the national standard for rigid cables was promulgated and implemented very early, which has strong constraints on the products of various manufacturers and fixed product models; The flexible cable market was chaotic before the introduction of the national standard.

However, both rigid and flexible cables can pass the most stringent C, W and Z tests in the British Standard Code for fire resistance of cables bs6387.
Finally, for the engineering design and application of mineral insulated cables, there is a problem that everyone is concerned about, that is, as pointed out in article 10.1.10-3 of code for fire protection design of buildings gb50016-2014 (2018 Edition), mineral insulated non combustible cables should be used for fire distribution lines.