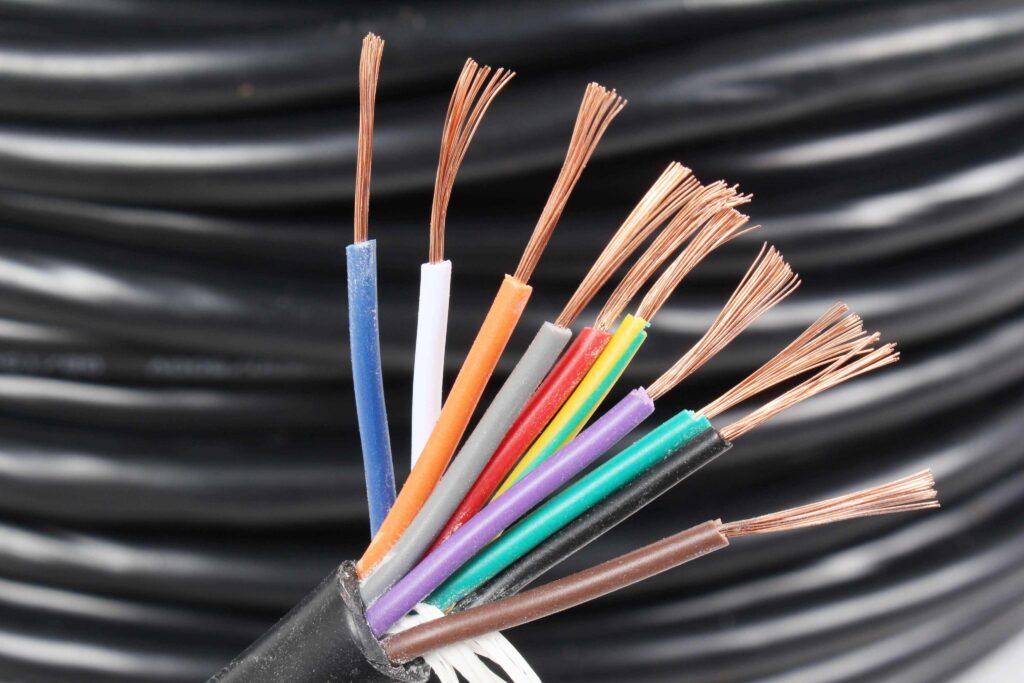
When selecting cables, the power cable line design, installation and operation departments shall consider four factors, such as cable service conditions, insulation level, AAAC Cable type and conductor section, which are divided as follows.
1. Cable service conditions
(1) cable rated voltage / u () shall meet the following requirements:
1) the voltage shall meet the requirements of neutral grounding mode of power system, that is, in the neutral ungrounded power system, the voltage of non fault phase increases by times in case of single-phase grounding fault, which is related to the troubleshooting time of system grounding fault.

In IEC standard, power system is divided into three categories. Class a means that any phase conductor of the system is grounded and can be separated from the system within lmin; Class B refers to the grounding of single-phase conductor in the system, the allowable grounding fault time shall not exceed 8h, and the annual cumulative time shall not exceed 125h; Class C is a system that does not belong to classes a and B.
when the cable is used in the neutral effective grounding system, u takes the phase voltage value of the system. For example, 6 / 10kV cable is selected for 10kV system and 21 / 35kV Cable is selected for 35kV system.
When the cable is used for neutral non effective grounding system, the cable with one level higher than the system phase voltage shall be selected. For example, 8.7/10kv cable shall be selected for 10kV system and 26 / 35kV Cable shall be selected for 35kV system.
When the cable is used in class C system and single-phase grounding is allowed for long-term operation, u shall select the line voltage of the system, such as 6 / 6kV cable in 6kV system.
2) the voltage U and shall be equal to or greater than the rated voltage and maximum working voltage of the system where the ACSR Cable is located.
(2) cable transmission capacity. The cable line must meet the transmission capacity of the power system, that is, the selected cable shall have long-term allowable current carrying capacity to meet the system requirements.
For longer cable lines, the line voltage drop of the cable shall also be considered.
(3) cable laying conditions. Cables shall adapt to different laying methods, arrangement methods, metal sheath grounding methods and surrounding medium temperature, etc. The conductor of XLPE cable used for underwater laying shall have longitudinal water resistance. In order to meet the requirements of various laying environments, such as tension, compression, fire prevention, termite prevention and rodent prevention, the armor layer and outer sheath of the cable shall be made of corresponding structural materials.

2. Basic insulation level of cable
the peak value of lightning impulse withstand voltage between each conductor of the cable and the shield or metal sheath, i.e. the basic insulation level bil, shall comply with the provisions in table 1-13.
picture
in table 1-13, the lightning impulse withstand voltage of 220kV and above cable lines has two values, which can be selected according to the protection characteristics of arrester, the characteristic length of impulse wave of cable line and the lightning impulse insulation level of connected equipment.
3. Cable type
(1) comparison of insulation properties between XLPE and oil paper cables. XLPE insulated cable has the advantages of simple production process, short manufacturing cycle, easy installation and maintenance, excellent electrical performance and large transmission capacity. In recent 30 years, the technology of XLPE insulated cable has developed very fast and has been widely used. In terms of insulation performance, compared with oil paper insulation, cross-linked polyethylene insulation has some different characteristics, which are listed in table 1-14.
picture
Note: “air raid” should be “gap”
Oil paper insulated cable has the advantages of excellent electrical performance and long service life. It can be used in general occasions. However, compared with XLPE cable, the manufacturing and installation process of oil paper ABC Cable is more complex and the cost is higher.
oil filled cable with paper plastic composite insulation with low dielectric loss and alkylbenzene synthetic oil with good aging resistance as insulation structure, suitable for voltage levels of 220kV and above. In addition, oil paper insulated cables are also suitable for HVDC transmission lines.
(2) for cable lines of 110kV and below, XLPE insulated cable is generally the preferred variety. For distribution cables of 1kV and below, in addition to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) insulated cables for lines with light load, cross-linked polyethylene insulated cables shall also be selected.
Note: at present, 1-500 cables are mainly XLPE cables, and only some stocks of oil paper insulated cables and oil filled cables are left.
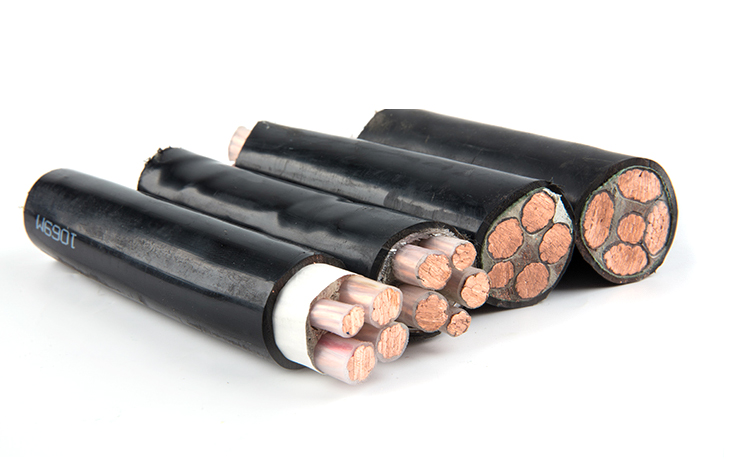

(3) ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) insulated cable is suitable for 35kV and below lines. This kind of cable is suitable for underwater laying because of its good moisture resistance, but its price is expensive.
4. Conductor section
copper conductors are generally used for power cables. The selection of conductor section shall meet the requirements of cable line transmission capacity and maximum short-circuit thermal stability of the system at the same time. And comply with “economic optimization of cable conductor size”.
in urban low-voltage power grid, four core cable is generally used, that is, in addition to three-phase conductor, there is a neutral line passing through three-phase unbalanced current and having protective grounding effect. The section of neutral wire shall generally be 30% ~ 60% of the conductor section of each phase. In the low-voltage power grid with large three-phase unbalanced current, four core low-voltage cables with equal cross-section shall be selected. The three core cable plus another insulated conductor cannot be used as the neutral wire to connect to the three-phase four wire low-voltage power grid, because in this way, there will be unbalanced current passing through the metal sheath and armor layer of the three core cable to heat it, thus affecting the transmission capacity of the cable.