2.1 catalytic aging of copper is an important reason for rubber hair adhesion
The experiment of the former Soviet Union Institute of AAAC Cable science proved that copper infiltrated into the insulating rubber from the contact with rubber during vulcanization, and the thickness of 1.0-2.0mm contained 0.009-0.0027% copper. As we all know, trace copper has a great damage to rubber, that is, heavy metal is the catalytic aging of rubber. During the process of insulation vulcanization, qiulanm precipitates some free sulfur to react with copper to form active copper containing groups: CH3 ■ ch2-ch-c-ch2- ■ ■ SS ■ ■ cucu, when aging, weak s-s-bond breaks, forming active copper containing base: cu-s-, which acts with rubber, and acts with oxygen, breaks down long bond molecules of rubber, making rubber soft and sticky, which is a combination of low molecular chain. The French Academy of rubber also pointed out that if there are harmful metals in rubber, such as copper, manganese and other heavy metal salts, the rubber viscosity will occur regardless of the type of promoter.
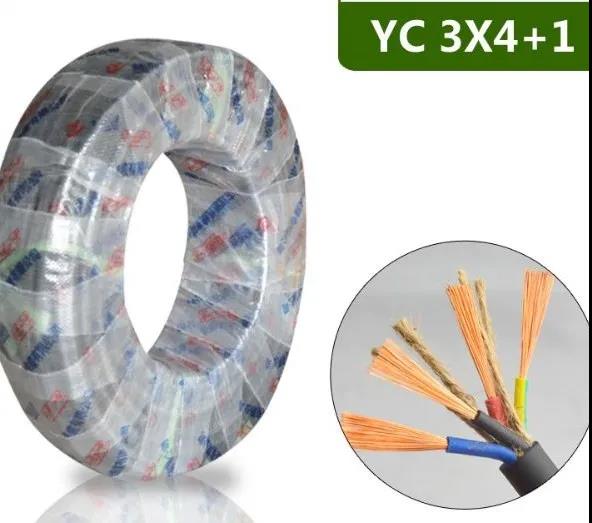

2.2 sulfur migration to the surface of insulating rubber and copper wire in rubber sheath cable
The possibility of sulfur diffusion in cable sheath rubber was confirmed by the use of radioisotope by former Soviet scientists. The diffusion coefficient of free sulfur is about 10-6cm2 / s at 130-150 ℃ in the vulcanized rubber based on natural rubber. In the continuous vulcanization factory, when vulcanizing sheath rubber, the temperature is between 185-200 ℃, and the diffusion coefficient is greater. Because of the diffusion of free sulfur in rubber sheath, the structure of the colum rubber is changed, and the polysulfide bond may be formed. These polysulfide compounds migrate through chemical decomposition and chemical combination, namely “chemical diffusion”. Due to the migration, not only the structure of the insulating rubber can be changed, the heat resistance of the rubber can be reduced, but the reaction between sulfur and copper surface will result in copper sulfide and cuprous sulfide, which leads to the blackening of copper wire. In turn, copper sulfide and cuprous sulfide accelerate the aging of rubber, and lead to the occurrence of adhesion.
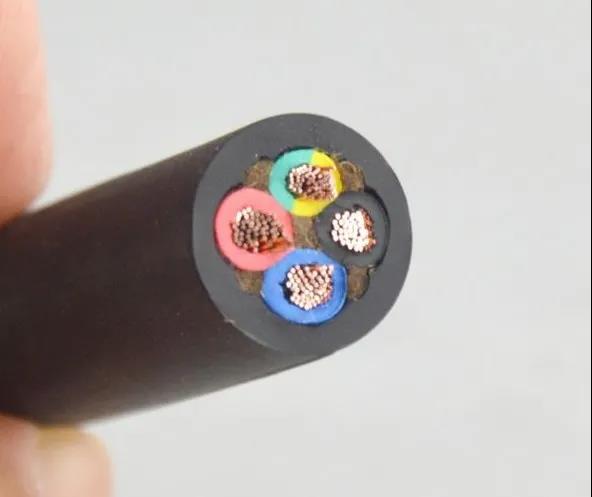

3. Reasons for processing technology
3.1 reasons for processing rubber
In the insulation formula based on the combination of natural rubber and SBR, the plastic of rubber needs to be improved by plastic refining. In order to produce, some factories use internal mixer to improve plasticity by adding a small amount of chemical plasticizer, accelerator M. If the temperature of plastic refining and rubber filtration are not well controlled, high temperature above 140 ℃ appears. When the raw rubber is put on the opening mill, it passes through the drum slowly. Because the rubber is affected by hot oxygen and accelerator M, it will be found that the rubber surface seems to be coated with oil. In fact, rubber molecules are more serious in promoting the chain breaking under the promotion of chemical plasticizer, A relatively soft and sticky rubber with smaller molecular weight was produced.
Although the rubber was mixed with SBR and then mixed with insulating rubber, these small molecular weight natural rubber were evenly dispersed in the rubber. After the rubber was extruded on the copper wire for continuous vulcanization, there might be no problem at that time, but a hidden danger was buried for the rubber copper ABC Cables. That is, the local copper wire sticking phenomenon will appear in the first place for these small molecular weight natural rubber.
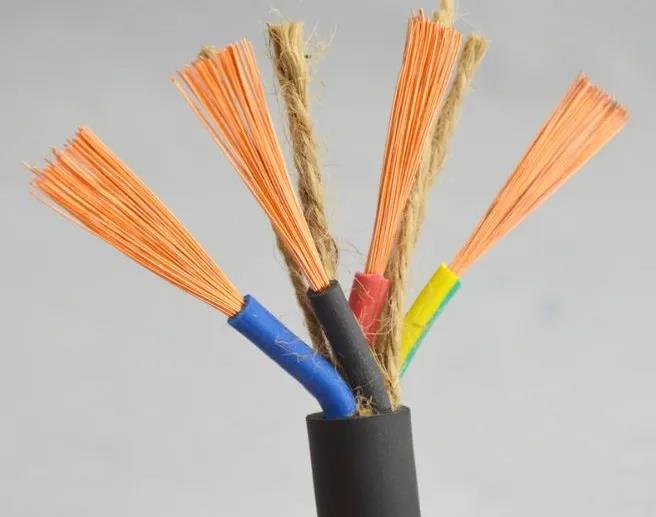

The process of adding vulcanizing agent and accelerator to insulating rubber is also very important. Some small factories add vulcanizing agent on the mixer, that is, pour the pot containing vulcanizate into the middle of the drum, with many in the middle, and less on both sides. When the vulcanizate into rubber, the number of turning triangle was less, which would make the vulcanizate distributed unevenly in the rubber. In this way, copper wire blackening is easy to appear in many places with vulcanizing agent when extrusion is continuous vulcanization. In the blackening place for a long time, the phenomenon of rubber adhesive copper wire will appear.
3.2 reasons for vulcanization of insulating rubber
In order to pursue the production, some enterprises only have 60 meters long continuous vulcanization tubes, 1.3mpa steam pressure, and the vulcanization speed is 120 m / min. thus, the residence time of insulating rubber in the pipe is only 30 seconds. Rubber itself is a bad conductor of heat. The surface temperature of the insulating core is more than 190 ℃, and when the temperature is transferred to the inner rubber contacting with copper wire, it is also absorbed by copper wire. When the copper wire is heated to close to the inner rubber temperature, the vulcanized rubber wire core has been discharged from the vulcanizing tube. So the temperature of the inner rubber is relatively low, about 170 ℃, and the vulcanization tube will be left only a few seconds. When it enters the cooling and winding, the insulation rubber will not be vulcanized enough.
In order to achieve sufficient vulcanization, the amount of promoter TMTD (as vulcanizing agent) is up to 3.4%. The excess of vulcanizing agent also releases more free sulfur during the curing process. Besides the crosslinking rubber molecules, there are also excess free sulfur. This is the reason why the copper wire surface is blackened.
In short, it is still difficult to solve the problem of copper wire blackening. Every process from copper wire to rubber should be taken seriously to achieve better results. The key to the problem is the choice of rubber species and the adoption of vulcanization system. The solution to this problem needs to go through the test of time.