Optical fibre cable is a communication cable consisting of two or more glass or plastic optical fiber cores located in a protective coating and covered by a plastic PVC outer sleeve. The signal transmission along the internal optical fiber generally uses infrared rays. In January 2013, Cuba carried out communications reforms, opening fiber optic cables and increasing foreign channels to attract attention.
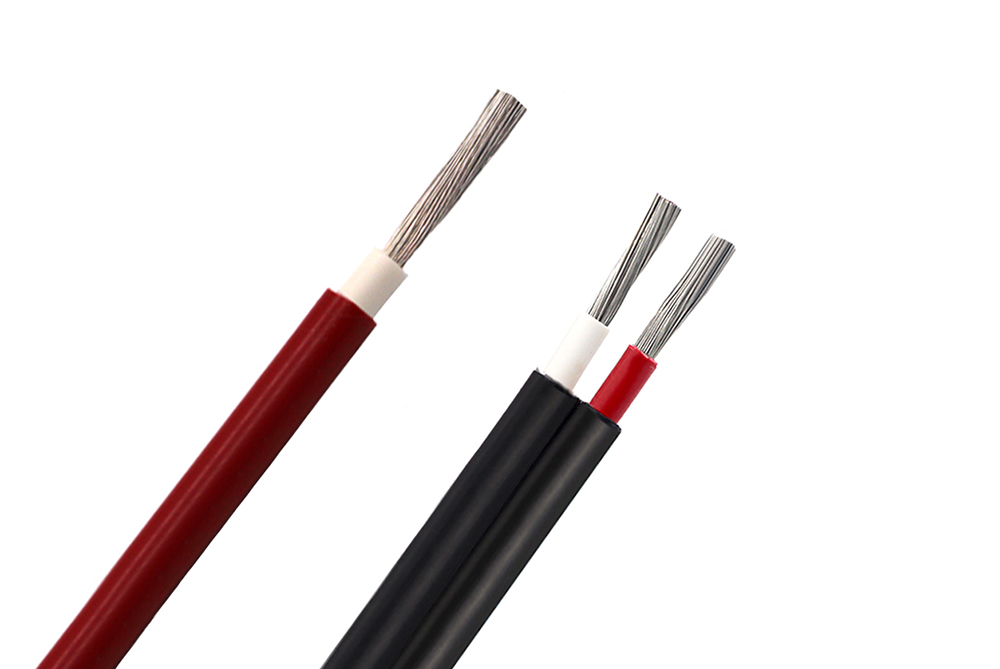
The difference between PV wire and ordinary cable
First: There is a difference in material. Cables use metal materials (mostly copper, aluminum) as conductors; optical fibers use glass fibers as conductors.
Second: There is a difference in the transmission signal. The cable transmits electrical signals. Optical fiber transmits optical signals.
Third: There are differences in the scope of application. Cables are now mostly used for energy transmission and low-end data information transmission (such as telephone). Optical fiber is mostly used for data transmission.
Recently, researchers from University College London demonstrated a new method of processing optical fiber cable signals. Researchers claim that this method can double the error-free transmission distance of signals through submarine fiber optic cables. Because the new method does not need to strengthen the signal, it has the potential to cut the cost of long-distance optical fiber communications.

The research was funded by the British Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council, and the research leader Robert Maher said: “By eliminating the interaction between optical channels, we can double the error-free signal transmission distance from 3190 kilometers to 5890 kilometers. This is also the largest distance increase reported in the system architecture. “The challenge is to design a technology that can simultaneously capture a group of optical channels with a single receiver, called a super channel.” Maher added.
They use a 16QAM (quadrature amplitude modulation) super channel, which contains a set of frequencies. These frequencies can be encoded using amplitude, phase, and frequency to create a high-capacity optical signal. Utilizing a high-speed super receiver and a new signal processing technology developed by the team that can receive all channels without errors, the super channels can then be detected.
Now, researchers plan to test new methods of dense super channels that are commonly used in digital cable television (64QAM), cable modems (256QAM), and Ethernet connections (1024QAM).
Polina Bayve, Professor of Optical Communications and Networking, added: “We are very pleased to report this important discovery, which will improve fiber optic communications. Our method can greatly increase the efficiency of data transmission, almost double the signal transmission distance, which may greatly reduce the existing The cost of commercial systems. One of the biggest global challenges we face is how to maintain communications under the prosperous Internet demand. Overcoming the capacity limitations of fiber optic cables is the key to solving the problem.”