Power cable section
The selection of power cable conductor cross-section should meet the following requirements:
1 The temperature of the cable bare conductor under the action of the maximum operating current shall not exceed the allowable value of the service life of the cable. Cable conductor work of continuous working loop
The temperature should meet the requirements of Appendix A of this code.
2 The temperature of the cable conductor under the action of the maximum short-circuit current and short-circuit time shall comply with the provisions of Appendix A of this code.
3 The voltage drop of the connected circuit under the maximum operating current shall not exceed the allowable value of the circuit.
4 In addition to meeting the requirements of paragraphs 1 to 3 above, the cross-section of power cables of 10kV and below should be based on the initial investment of the cable and the operation during its service life.
The principle selection of comprehensive cost economy. The selection method of economical current cross-section for power cables of 10kV and below should comply with the regulations in Appendix B of this code.
5 The minimum cross-section of multi-core power cable conductors, copper conductors should not be less than 2.5mm2, and all aluminum conductors should not be less than 4mm2.
6 For cables laid underwater, when the conductor is required to withstand the tensile force and is reasonable, the cross section can be selected according to the tensile requirements.
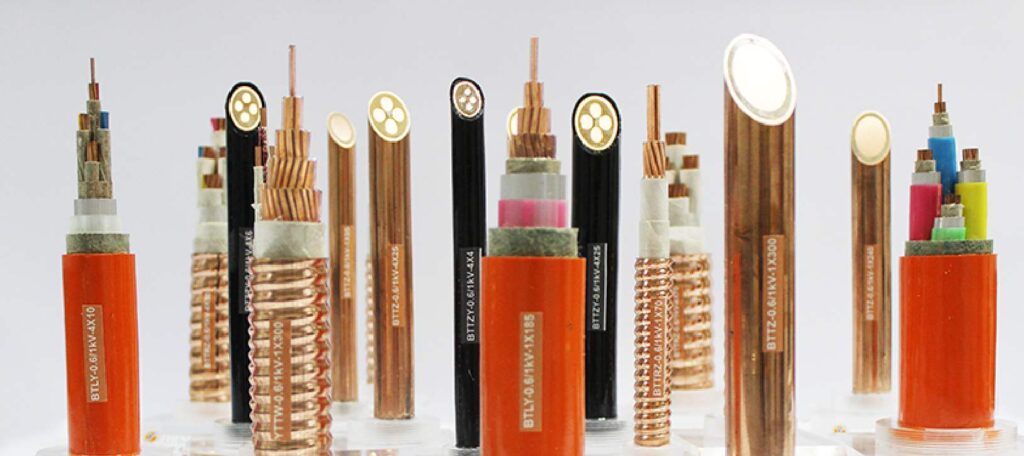

Commonly used cables of 10kV and below shall determine the allowable minimum cross-section of the cable conductor at 100% continuous working current, which should meet the requirements of Appendix C and Appendix D of this code. The current carrying capacity shall be greater than The working current of the loop.
1 Difference in ambient temperature.
2 The difference in soil thermal resistance coefficient when directly buried.
3 The influence of multiple parallel cables.
4 The influence of sunlight on outdoor overhead laying without shading.
Except for the conditions specified in Article 3.7.2 of this code, when the cable determines the minimum allowable cross-section of the cable conductor at 100% continuous working current, it shall be verified by calculation or test, and the calculation content or parameter selection shall meet the following requirements:
1 Non-coaxial cables used in power supply circuit cables with higher harmonic loads or intermediate frequency load circuits should be included in the skin effect and the increase in proximity effect
And other additional heating effects.
2 For single-core high-voltage cables that are cross-connected and grounded, when the three sections in the unit system are of unequal length, the effect of the additional loss and heating of the metal layer should be included.
3 The cables laid in the protective tube shall be included in the influence of thermal resistance; the cables with different holes in the pipe shall also be included in the influence of mutual heating factors.
4 Cables laid in closed, semi-enclosed or ventilated refractory trough boxes should be included in the heat resistance of the type of material and the thickness and size of the box.
The impact of increased resistance.
5 When the thickness of the fireproof coating, tape and other covering layer applied on the cable is greater than 1.5mm, the thermal resistance should be included.
6 When the cable in the trench is buried with sand and there is no regular water supplement, a thermal resistance coefficient greater than 2.0K·m/W should be selected according to the sand quality to include the influence on the increase of the thermal resistance of the cable.
When calculating the continuous allowable current-carrying capacity of the cable whose conductor working temperature is greater than 70℃, the following requirements should be met:
1 When a large number of such cables are laid in tunnels and shafts without mechanical ventilation, the impact on environmental temperature rise should be included.
2 Cables are directly buried in dry or moist soil. Except for the implementation of soil replacement treatment to avoid water migration, the soil thermal resistance coefficient is not
It should be less than 2.0K·m/W.